

Note, however, that the cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution should not be confused with its density function (the bell curve), which simply assigns the probability value to all of the arguments: φ(x) = 1/√(2π) * exp(-x 2/2)īy definition, the density function is the first derivative, i.e., the rate of change of the normal CDF. You can also use this calculator as a normal CDF calculator! Make sure to check out the p-value calculator for more information on this topic.

Similarly, if you want to find the probability of the variable being higher than X, you should integrate this function from X to infinity. In that case, you should integrate this function from minus infinity to X.

You can either use the normal distribution table or try integrating the normal cumulative distribution function (normal CDF): Φ(x) = 1/√(2π) * ∫ exp(-t 2/2) dtįor example, suppose you want to find the probability of a variable being lower than X. This mathematical beauty is precisely why data scientists love the Gaussian distribution!Ĭalculating the area under the graph is not an easy task. The right-hand tail and the left-hand tail of the normal distribution are symmetrical, each with an area of 0.16. You can see that the remaining probability (0.32) consists of two regions. Let's take another look at the graph above and consider the distribution values within one standard deviation. You can calculate the probability of your value being lower than any arbitrary X (denoted as P(x < X)) as the area under the graph to the left of the z-score of X. That means that it corresponds to probability. The total area under the standard normal distribution curve is equal to 1. If you input the mean, μ, as 0 and standard deviation, σ, as 1, the z-score will be equal to X. You can check that this tool by using the standard normal distribution calculator as well.
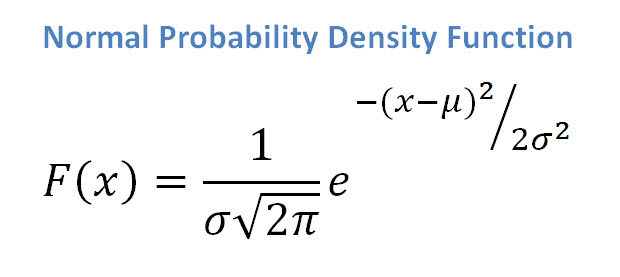
As this distribution is symmetric about the center, 50% of values are lower than the mean, and 50% of values are higher than the mean.Īnother parameter characterizing the normal distribution is the standard deviation. In a normal distribution, the mean value ( average) is also the median (the "middle" number of a sorted list of data) and the mode (the value with the highest frequency of occurrence). Many observations in nature, such as the height of people or blood pressure, follow this distribution. Most data is close to a central value, with no bias to left or right. Normal distribution (also known as the Gaussian) is a continuous probability distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
